..
938. Range Sum of BST
Problem Description
Given the root node of a binary search tree and two integers low and high, return the sum of values of all nodes with a value in the inclusive range [low, high].
Example 1:
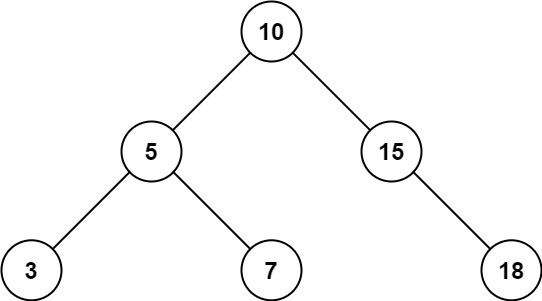
Input: root = [10,5,15,3,7,null,18], low = 7, high = 15
Output: 32
Explanation: Nodes 7, 10, and 15 are in the range [7, 15]. 7 + 10 + 15 = 32.
Example 2:
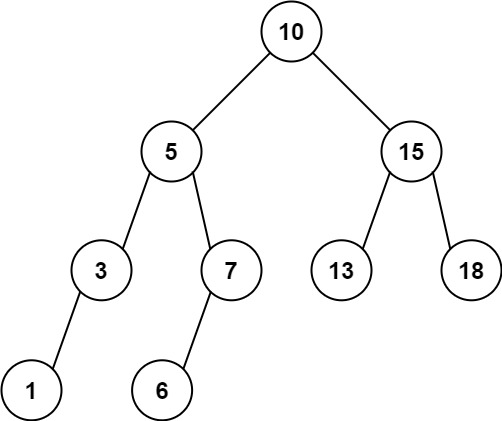
Input: root = [10,5,15,3,7,13,18,1,null,6], low = 6, high = 10
Output: 23
Explanation: Nodes 6, 7, and 10 are in the range [6, 10]. 6 + 7 + 10 = 23.
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 2 * 104].
1 <= Node.val <= 105
1 <= low <= high <= 105
All Node.val are unique.
Solution
This is an easy level question, but still there are some key points during the thought process:
- First, this is a BST, and the question give you an inclusive range.
- You might consider that you can use the attribute of BST which is left child node is less than the root and right child node greater than or equal to root node.
- Based on
#1, then you might consider split the range, for example.sum([1..99])equals tosum([1..49]) + 50 + sum([51..99])
If you already reach this far, then you have already successfully figured out how to solve this problem, the next step is just to find out the way to implement this.
Divide & Conquer
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def rangeSumBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], low: int, high: int) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
if root.val > high:
return self.rangeSumBST(root.left, low, high)
if root.val < low:
return self.rangeSumBST(root.right, low, high)
return (
root.val
+ self.rangeSumBST(root.left, low, root.val)
+ self.rangeSumBST(root.right, root.val, high)
)
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity
- O(h), where h is the height of the BST, worst case is O(n)
- Space Complexity
- O(1)
Runtime: 216 ms, faster than 58.13% Memory Usage: 22.3 MB, less than 59.19%