Choose the right database:
- balanced workload or heavy-read or heavy-write?
- throughput, does it fluctuate or something predictable
- how much data to store, how long? average object size
- data durability
- latency requirement
- data model
- strong schema or flexible, SQL or NoSQL
- License costs
Database types which are supported by AWS:
- Relational Database
- RDS
- Postgres
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- Oracle
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Aurora (* AWS Proprietary database)
- RDS
- NoSQL
- DynamoDB (~ JSON)
- ElastiCache (key-value pairs)
- Neptune (graphs) - no joins, no SQL
- Object Store (“sort of”)
- S3
- Glacier
- Data Warehouse
- Redshift
- Athena (query data in S3 using SQL, so “sort of”)
RDS Overview
RDS is a managed service:
- Automated provisioning, OS patching
- Continuous backups and restore to specific timestamp (Point in Time Restore)
- Monitoring dashboard
- Read replicas for improved read performance
- Multi-AZ setup for Disaster Recovery
- Maintenance windows for upgrades
- Scaling capability (vertical and horizontal)
- Storage backed by EBS (gp2 or io1)
BUT, you cannot SSH into your instances
There are two important features for RDS
- Multi-AZ: this is for “Disaster Recovery”
- Read Replicas: this is for “Improving Performance”
OLTP vs OLAP
OLAP is for Data Warehousing on AWS (a different type of architecture both from a database perspective and infrastructure layer)
ElasticCache
This is a service for a web app, it is easy to deploy, operate, and scale an in-memory cache in the cloud.
It speeds up the performance of existing databases’ frequent identical queries
RedShift
This is for BI / Data warehousing -> OLAP usage
Relational Database
- RDS runs on a virtual machine, but you cannot ssh to it
- RDS is NOT serverless, BUT Aurora Serverless IS Serverless
RDS - Backups, Multi-AZ & Read Replicas
Backups
There are two types of Backups for RDS
- Automated Backups
- Database Snapshots
Automated Backups
It allows users to recover your database to any point in time within a “Retention Period”, this is around 7 ~ 35 days.
Automated backup is enabled by default, the backup data is stored in S3, meanwhile, the size of your RDS is equal to the size of S3
Automated backups:
- Daily full backup of the database (during the maintenance window)
- Transaction logs are backed-up by RDS every 5 minutes
- This gives the ability to restore to any point in time (from oldest back-up to 5 minutes ago)
Database Snapshot
Database Snapshot is stored even after you delete the original RDS Instance
But it is manually triggered by the user, and retention of backup for as long as you want
Multi-AZ
- It has only one DNS name, automatic app failover to standby, no manual intervention in apps
- This is an exact copy of your production database in
another AZ - Automatically synchronized when your prod database is written to
- In the event of the following:
- planned database maintenance
- DB instance failure
- AZ failure
- Network failure
This is only for Disaster Recovery, increase availability
Read Replicas
This allows you to have a read-only copy of your production database.
This is achieved by using asynchronously replication from the primary RDS Instance to the Read Replicas. It is better for those databases with heavy read workloads
Read replicas are used for SELECT (or read) the only kind of tasks, not INSERT, DELETE or UPDATE
Be careful of the difference between Read Replicas and the previous database backup methods
- Read Replica is for scaling, for performance improvements
- To use Read Replicas, you should turn on the setting for "Automated Backups"
- You can have up to 5 Read replicas of any database
- You can even have Read replicas of Read replicas
- Each Read replicas has its Endpoint
- Read replicas can be prompted to be their database, but replications won't work
Read Replicas - Network Cost
In AWS, there is a network cost when data goes from one AZ to another, so to reduce cost, you can have your Read Replicas in the same AZ
RDS Securities
Encryptions
This is achieved by using AWS KMS (Key Management Service), once the encryption is on, the followings are encrypted:
- data underlying storage
- automated backups
- read replicas
- database snapshots
Whenever you restore either an Automated Backup or Database Snapshot, the restored version of the database will be a new RDS instance with a new DNS endpoint
At rest encryption and In-flight encryption
At rest encryption
We can encrypt the primary DB and read replicas with AWS KMS - AES - 256 encryption, this has to be defined at launch time.
If the primary DB is not encrypted, the read replicas cannot be encrypted
or, unencrypted DB -> snapshot -> copy snapshot as encrypted -> create new DB from encrypted snapshot
Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) available for Oracle and SQL Server
In-flight encryption
This allows to use SSL Certificates to encrypt data to RDS in flight, you have to provide SSL options with trust certificate when connecting to the database
Network & IAM
Network Security
- RDS databases are usually deployed with a private subnet, not in a public one
- RDS security works by leveraging security groups, it controls which IP / security group can communicate with RDS
Access Management
- IAM policies help control who can manage AWS RDS through the RDS API, like “who can create a read replica? etc..”
- traditional username/password can be used to log into the database
- IAM-based authentication can be used to login to RDS MySQL & PostgreSQL
IAM Authentication
- works with MySQL & PostgreSQL
- no need for a password, just a token obtained through IAM & RDS API call
- the token has a lifetime of 15 minutes
the IAM Authentication has the following benefits:
- Network in/out must be encrypted using SSL
- IAM to centrally manage users instead of DB
- Can leverage IAM Roles and EC2 Instance profiles for easy integration
Aurora
Aurora is the MySQL compatible, AWS solution to Relational Database
Aurora HA and Scalability
Aurora always maintains 2 copies of your data in each AZ, with a minimum of 3 AZ => which leads to 6 copies of your data
Among these 6 copies of your data across 3 AZ:
- 4 copies out of 6 needed for writes
- 3 copies out of 6 needed for reads
- self-healing with peer-to-peer replication
- storage is striped across 100s of volumes
There is a primary-secondary architecture, one Aurora instance will take writes (primary)
If there is a failover happened, the automated failover for primary DB will take effect in less than 30 seconds
You can have up to 15 Aurora Read Replicas serve reads, the read replicas support Cross Region Replication
Aurora Replicas
There are 2 types of Aurora Replicas
- Aurora Replicas
- MySQL Read Replicas
Automated failover is only available with Aurora Replicas
Backups for Aurora, also 2 types:
- Automated Backups
- Data Snapshots
To migrate data from MySQL to Aurora, you can do the following things
- take a data snapshot and restore in Aurora
- create an Aurora Read replica and then promote the Read Replica as a "database service"
Aurora DB Cluster
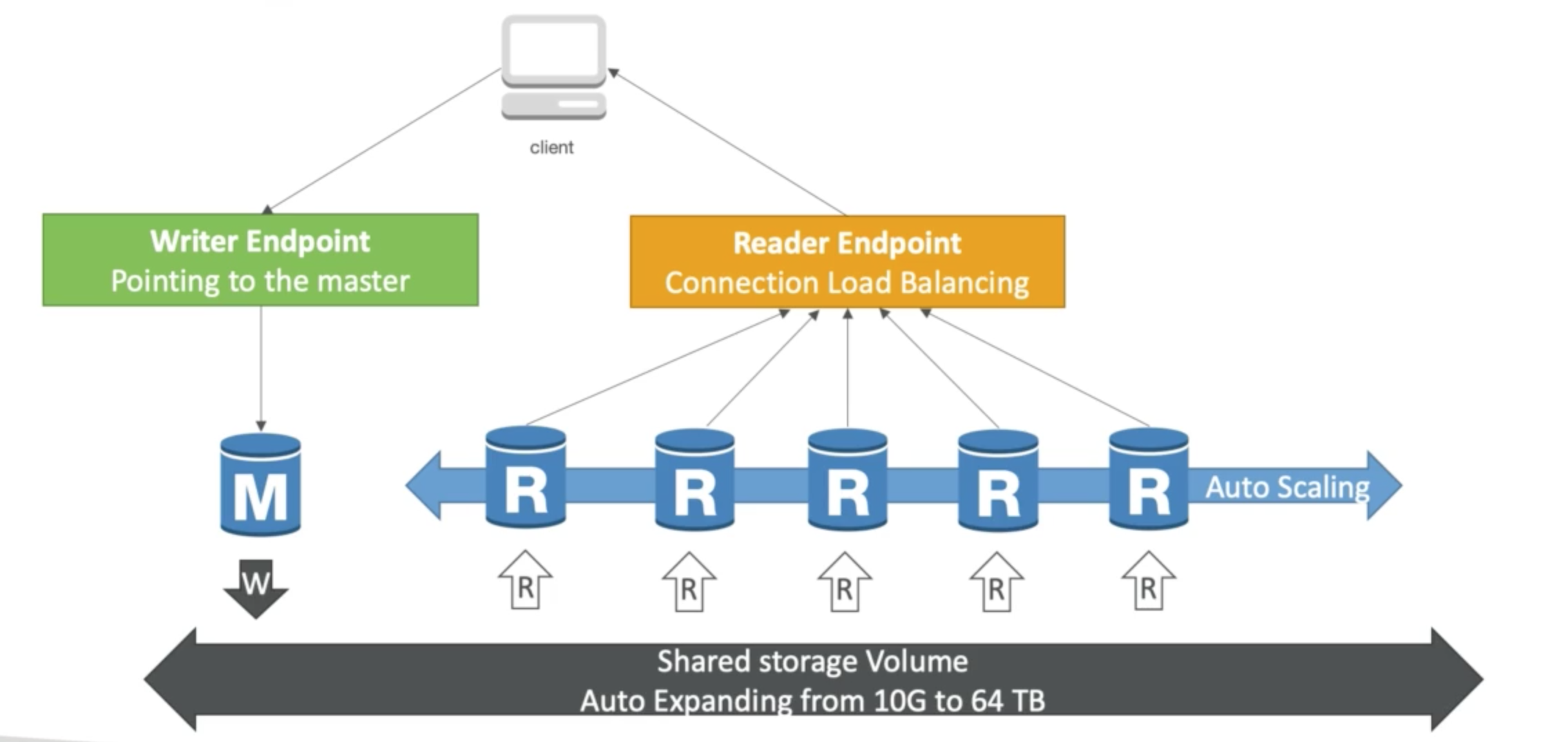
load balancing happens during connection
Aurora Serverless
- Automated database instantiation and autoscaling based on actual usage
- good for infrequent, intermittent, or unpredictable workloads
- no capacity planning needed
- pay per second, can be more cost-effective
Aurora Serverless will create Aurora instance, and the client will connect to Aurora with
Proxy Fleet, with auto-scaling turned on, which means: if the QPS is large, then more Aurora instances will be created, otherwise, will be deleted
Global Aurora
- Aurora Cross Region Read Replicas
- Useful for disaster recovery
- Simple to put in place
- Aurora Global Database (recommended)
- 1 Primary Region (read / write)
- Up to 5 secondary (read-only) regions, replication lag is less than 1 second
- Up to 16 Read Replicas per secondary region, helps for decreasing latency
- Promoting another region (for disaster recovery) has an RTO (Recovery Time Objective) of < 1 minute
ElastiCache
This is the AWS solution to the web-service-based in-memory cache
ElasticCache Overview
- The same way RDS is to get managed Relational Databases
- ElastiCache is to get managed Redis or Memcached
- Helps reduce the load off of databases for reading-intensive workloads
- Make application stateless
- Write Scaling using Sharding
- Read Scaling using Read Replicas
- Multi-AZ with failover Capability
- AWS takes care of OS maintenance/patching, optimizations, setup, configuration, monitoring, failure recovery, and backups
DB Cache

Application queries ElastiCache first, if data is not available (cache miss) then get data from RDS and store in ElastiCache, so that for the later queries, it will reach cache hit
User Session Store
- User login to any of the application
- The application writes the session data into ElastiCache
- The user hits another instance of our application
- The instance retrieves the data and the user is already logged in
ElastiCache - Redis or Memcached
| Redis | Memcached |
|---|---|
| Multi-AZ with Auto-Failover | Multi-node for the partitioning of data (sharding) |
| Read Replicas to scale reads and have high availability | Nonpersistent |
| Data Durability using AOF persistence | No backup and restore |
| Backup and restore feature | Multi-threaded architecture |
- If you need scale horizontally, you need to choose Memcached
- If you need Multi-AZ, Backups, and Restores, you need to choose Redis
Right now, we have two methods of improving performance
- ElasticCache -> Cache layer to speed up
- Read Replicas -> Improved read/write on the database layer
ElastiCache - Cache Security
All caches in ElastiCache:
- support SSL in-flight encryption
- Do not support IAM authentication
- IAM policies on ElastiCache are only used for AWS API-level security
Redis AUTH
- You can set a “password/token” when you create a Redis Cluster
- This is an extra level of security for your cache (on top of Security Group)
Memcached
- Supports SASL-based authentication
ElastiCache for Solutions Architects
Patterns for ElastiCache
- Lazy Loading: all the read data is cached, data can become stale in the cache
- Write Through: Adds or Update data in the cache when written to a DB (no stale data)
- Session Store: store temp session data in the cache (using TTL features)
DynamoDB
DynamoDB can do transactions now
DynamoDB is AWS solution for Serverless NoSQL datbase, it supports document and key-value pair data models
- data is stored ion SSD Storage
- High available with replication across 3 AZ (geographically distinct data centers)
- Eventually Consistent Reads (Default)
- Strongly Consistent Reads
Eventually Consistent Reads
Consistency across all copies of data is usually reached within a second. Repeating a read after a short time should return the updated data.
This is for "Best Read Performance", this setting is enabled by default
Strongly Consistent Reads
A Strongly Consistent Read returns result that reflects all writes that received a successful response before the read
DynamoDB - Basics
- DynamoDB is made of tables
- Each table has a primary key (must be decided at creation time)
- Each table can have an infinite number of items (= rows)
- Each item has attributes (can be added over time - can be null)
- Maximum size of an item is 400 KB
DynamoDB - Provisioned Throuput
- Table must have provisioned read and write capacity units
- Read Capacity Units (RCU): throughput for reads
- 1 RCU: 1 strongly consistent read of 4 KB per second
- 1 RCU: 2 eventually consistent read of 4 KB per second
- Write Capacity Units (WCU): throughput for writes
- 1 WCU: 1 write of 1 KB per second
- Option to set up auto-scaling of throughput to meet demand
- Throughput can be exceeded temporarily using “burst credit”
- If burst credit is empty, you’ll get a
"ProvisionedThroughputException" - It’s then advised to do an exponential back-off retry
DynamoDB - DAX
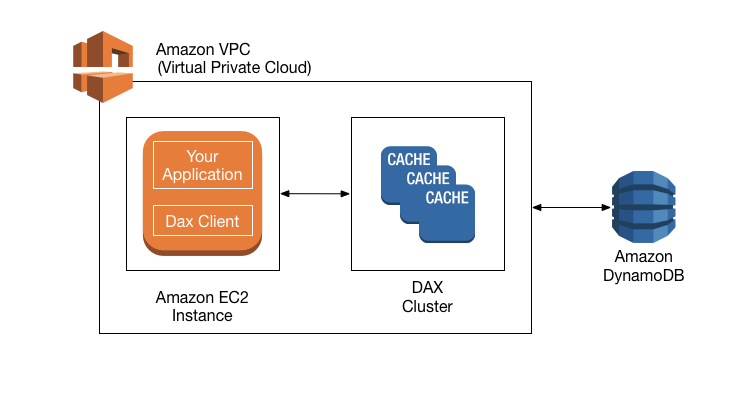
DAX is DynamoDB Accelerator, it provide seamless cache for DynamoDB, no application re-write needed. Writes go through DAX then to DynamoDB.
Multi-AZ is supported, 3 nodes minimum recommended for production
DynamoDB Streams
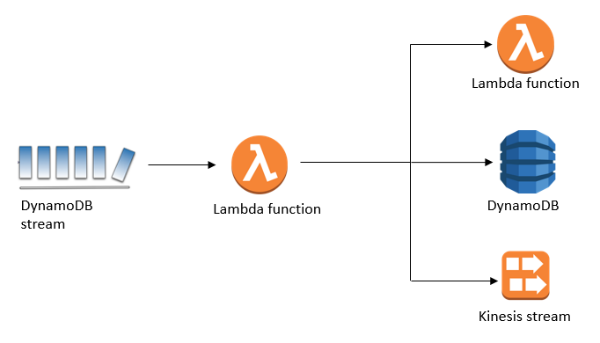
- Changes in DynamoDB will end up in a DynamoDB Stream
- This stream can be read by AWS Lambda, so we can do analytical jobs
- Could implement cross-region replication using Streams
- It has 24 hours of data retention
DynamoDB - Security
- VPC Endpoints available to access DynamoDB without internet
- Access fully controlled by IAM
- Encryption: KMS and SSL/TLS
DynamoDB - Other Features
Global Tables:
- Active-Active replication in many regions
- Must enable DynamoDB Streams
- It is Low-latency, for Disaster Recovery
Capacity Planning:
- Planned capacity: provision WCU & RCU can enable auto-scaling
- ON-demand capacity: get unlimited WCU & RCU, no throttle, more expensive
rare workloads - on-demand capacity
predictable workloads which can be auto-scaled - planned capacity
other features like, backup & restore, migration and you can even set up a local DYnamoDB for development
RedShift
This is the AWS solution to Data Warehousing service, it supports Massively Parallel Processing (MPP)
Backups for RedShift
- this is enabled by default and it has 1 day retention period, and the maximum is 35 days
- always attempt to maintain at least 3 copies of your data, the original or the replicas on the compute node, the backups are on AWS S3
But it is only available in one AZ
Neptune
Fully managed graph database
- high relationship data
- social network
- knowledge graph
Highly available across 3 AZ, with up to 15 read replicas, with point-in-time recovery, continuous backup to Amazon S3. Support KMS encryption at rest + HTTPS
