KMS, Encryption SDK, SSM Parameter Store
Why encryption?
Encryption in flight (SSL)
- Data is encrypted before sending and decrypted after receiving
- SSL certificates help with encryption
- Encryption in flight ensures no MITM (man in the middle attack) can happen
Server-side Encryption at rest
- Data in encrypted after being received by the server
- Data is decrypted before being sent
- It is stored in an encrypted form
- The encryption/decryption keys must be managed somewhere and the server must have access to it
Client-side encryption
- Data is encrypted by the client and never decrypted by the server (gpg)
- Data will be decrypted by a receiving client
- The server should not be able to decrypt the data
- Could leverage Envelope Encryption
AWS KMS (Key Management Service)
AWS KMS provides an easy way to control access to your data, AWS manages keys for you. It is also fully integrated with IAM for authorization
It seamlessly integrated into:
- EBS: encrypt volumes
- S3: server-side encryption of objects
- RedShift / RDS: encrypt data
- SSM: Parameter store
Anytime you need to share sensitive information, use KMS
The value in KMS is that the CMK used to encrypt data can never be retrieved by the user, and the CMK can be rotated for extra security
CMK - Customer Master Keys
- Never store your secrets in plaintext, especially in your code
- KMS can only help in encrypting up to 4KB of data per call, if data is greater than 4KB, use Envelope Encryption
To give access to KMS to someone:
- make sure the Key Policy allows the user
- make sure the IAM Policy allows the API Calls
KMS Functionality
- Able to fully manage the keys & policies, Create, Rotation policies, Disable, Enable
- Able to audit key usage (with CloudTrail)
- Three types of Customer Master Keys (CMK):
- AWS Managed Service Default CMK - free
- User Keys created in KMS - $1 / month
- User keys imported (must be 256-bit symmetric key) - $1 / month
- Additional pay for API Calls to KMS ($0.03 / 10000 calls)
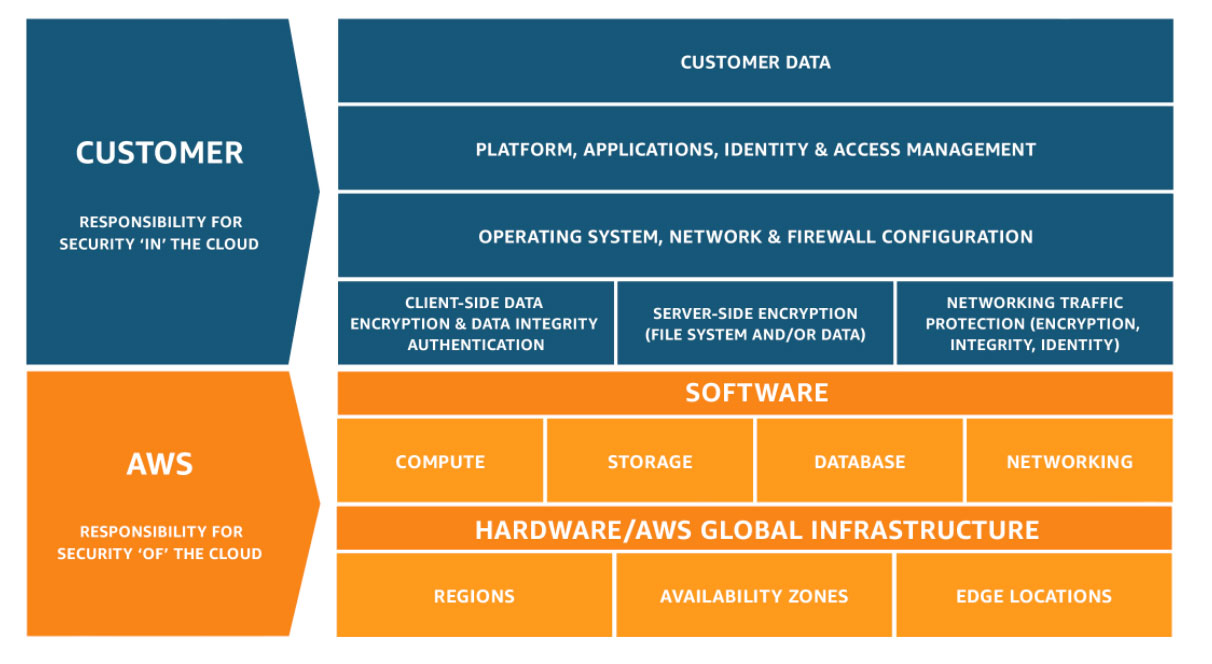
KMS API - Encrypt and Decrypt
All the encryption and decryption happen inside of KMS, and it will check for the IAM permissions
Encryption in AWS Services
Requires migration (Snapshot + Backup)
- EBS Volumes
- RDS Databases
- ElastiCache
- EFS network file system
In-place encryption
- S3
AWS SSM Parameter Store
- Secure storage for configuration and secrets
- Optional Seamless Encryption using KMS
- Version tracking of configurations/secrets
- Configuration management using path & IAM
- Integration with CloudFormation
AWS Parameter Store has a “tree” structure, which means it can have similar structure to the below:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
/my-app
/dev
/db-password
/db-username
/prod
/db-username
/db-password
/test
....
Example of using SSM with Lambda:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
import json
import boto3
ssm = boto3.client("ssm", region_name="us-west-1")
def lambda_handler(event, context):
db_url = ssm.get_parameters(Names=["/my-app/dev/db-url"])
db_pwd = ssm.get_parameters(Names=["/my-app/dev/db-pwd"], WithDecryption=True)
return [db_url, db_pwd]
serveral settings for IAM role to make the above example work:
ssm.get_parameters(Names=["/my-app/dev/db-url"])- IAM Policies for SSM,getParametersssm.get_parameters(Names=["/my-app/dev/db-pwd"], WithDecryption=True)- IAM Policies for KMSDecrypt
AWS Secrets Manager
- newer service for storing secrets
- it can
force rotation of secretsevery X days - automate the generation of secrets on rotation (uses Lambda)
- integration with Amazon RDS (MySQL, PostgreSQL, Aurora)
- secrets are encrypted using KMS
secrets rotation, RDS integration - secrets manager
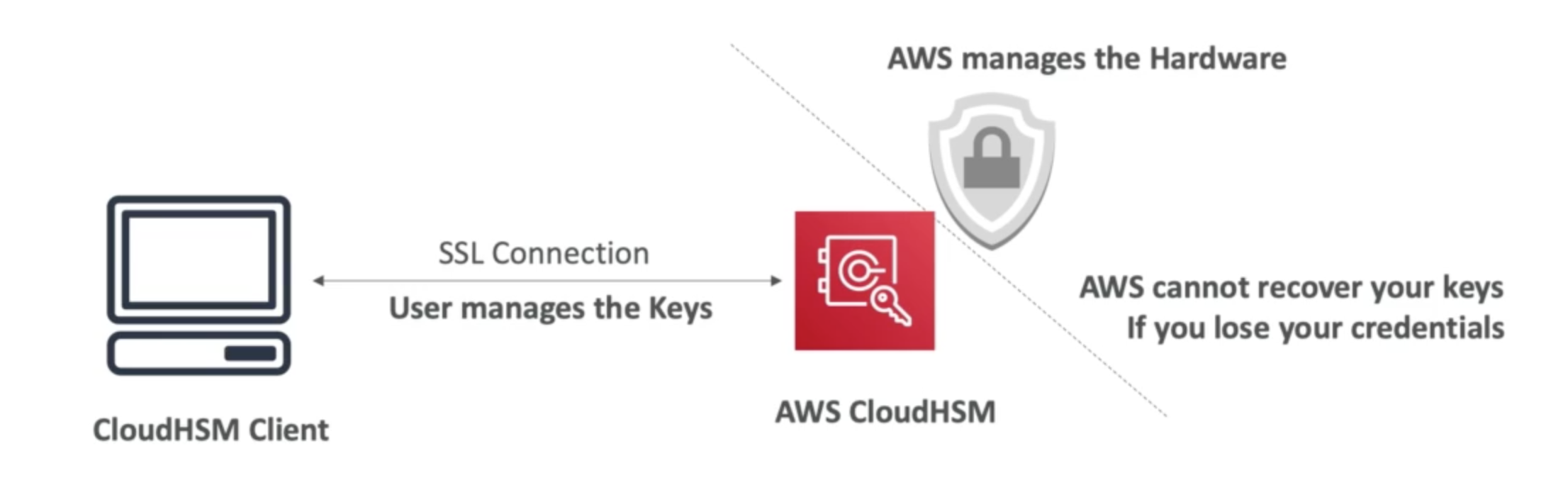
CloudHSM
KMS -> AWS manages the software for encryption CloudHSM -> AWS provisions ecryption hardware
- It provides dedicated Hardware (HSM represents Hardware Security Module)
- You manage your encryption keys entirely
- HSM device is tamper-resistant
- CloudHSM clusters are spread across Multi-AZ (HA), you must set up first
- Supports both symmetric and asymmetric encryption (SSL/TLS keys)
No free tier Must use the CloudHSM Client Software - With the option to use with SSE-C encryption
- IAM Permissions: CRUD an HSM Cluster
- CloudHSM Software: Manage the Keys and Users
AWS Shield - DDoS Protection
AWS Shield Standard
This is a free service, activated for every AWS customer. It protects from attacks such as SYN/UDP Floods, Reflection attacks, and other layer 3 / layer 4 attacks
AWS Shield Advanced
This provides an optional DDoS mitigation service ($3000 per month per organization). It protects against more sophisticated attack on EC2, ELB, CloudFront, AWS Global Accelerator and Route53
It can protect against higher fees during usage spikes due to DDoS
AWS WAF - Web Application Firewall
- Protects your web application from common web exploits (layer 7)
- Deploy on Application Load Balancer, API Gateway, CloudFront
- Define Web ACL (Web Access Control List):
- Rules can include IP addresses, HTTP headers, HTTP body, or URI strings
- Protects from common attack - SQL injection and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- Size constraints, Geo match
- Rate-based rules (to count occurrences of events)
AWS Firewall Manager
- Manage rules in all accounts of an AWS Organization
- Common set of security rules
- WAF rules
- AWS Shield Advanced
- Security Groups for EC2 and ENI resources in VPC
Sample Reference Architecture for DDoS Protection

References: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/aws-best-practices-ddos-resiliency/mitigation-techniques.html
Shared Responsibility Model
Take RDS for example:
| AWS Responsibility | YOUR Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Manage the underlying EC2 instance, disable SSH access | Check the ports / IP / SG inbound rules in DB’s SG |
| Automated DB / OS Patching | In-database user creation and permissions |
| Audit the underlying instance and disks & guarantee it functions | Creating a database with or without public access |
| etc.. | Ensure parameter groups or DB is configured to only allow SSL connections |
| Database encryption setting | |
| etc.. |