What is serverless?
serverless was pioneered by AWS Lambda but now also includes the idea that “no self-managed databases, messaging, storage, etc..”
AWS Lambda
Why do we use AWS Lambda?
with AWS Lambda:
- virtual functions - no servers to manage
- limited by time - short executions
- run on-demand
- scaling is automated
AWS Lambda Configuration
- Timeout: default 3 seconds, max of 15 minutes (900 seconds)
- Support environment variables
- Allocated memory (range: 128 MB to 3 GB)
- Ability to deploy within a VPC + assign security groups
- IAM execution role must be attached to the Lambda function
AWS Lambda Limits to Know
Execution
- Memory allocation: 128 MB to 3008 MB (64 MB increments)
- Maximum execution time: 300 seconds (5 minutes)
- Disk capacity in the “function container”: 512 MB
- # of Concurrency limits: 1000
Deployment
- Lambda function deployment size (compressed
.zip): 50 MB - Size of uncompressed deployment (code + dependencies): 250 MB
- Can use the
/tmpdirectory to load other files at startup - Size of environment variables: 4 KB
Lambda@Edge
With Lambda@Edge, you can deploy Lambda functions alongside your CloudFront CDN
- Build more responsive applications
- You don’t manage servers, Lambda is deployed globally
- Customize the CDN content
- Pay only what you use
API Gateway
API Gateway is a fully managed service that makes it easy for developers to publish, maintain, monitor, and secure APIs at any scale.
- Expose HTTPS endpoints to define a RESTful API
- Serverless-ly connect to services like Lambda \& DynamoDB
- Send each API endpoint to a different target
- Run efficiently with low cost
- Scale effortlessly: scale automatically along with your traffic
- Track and control usage by API key
- Throttle requests to prevent attacks
- Connect to CloudWatch to log all requests for monitoring
- Maintain multiple versions or environments of your API
- Support Swagger / Open API to import
- Caches available
We can enable API caching to cache your endpoint’s response. With caching, we can reduce the number of calls made to your endpoint and also improve the latency of the requests to your API. When you enable caching for a stage, API Gateway caches from your endpoint for a specified time-to-live (TTL) period, in seconds. API Gateway then responds to the request by looking up the endpoint response from the cache instead of requesting your endpoint.
API Gateway Integrations
Outside of VPC
- AWS Lambda (*)
- Endpoints on EC2
- Load Balancers
- Any AWS Services
- External and publicly accessible HTTP endpoints
Inside of VPC
- AWS Lambda in your VPC
- EC2 Endpoints in your VPC
API Gateway - Security
- Cross-Site Scripting: In computing, the same-origin policy is an important concept in the web application security model. Under the policy, a web browser permits scripts contained in a first web page to access data in a second web page, but only if both web pages have the same origin. This will prevent cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.
- CORS: CORS is one way the server at the other end (not the client code in the browser) can relax the same-origin policy. Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) is a mechanism that allows restricted resources (e.g. fonts) on a web page to be requested from another domain outside the domain from which the first resource was served.
IAM Permissions
- Create an IAM policy authorization and attach it to User / Role
- API Gateway verifies IAM permissions passed by the calling application
- Good to provide access within your infrastructure
- Leverages
"Sig v4"capability where IAM credentials are in headers
"Sig v4", API show up in the exam, it may be related to IAM PermissionsLambda Authorizer
- Uses AWS Lambda to validate the token in the header being passed
- Option to cache result of authentication
- Helps to use OAuth / SAML / 3rd party type of authentication
- Lambda must return an IAM policy for the user
Cognito User Pools
- This utilizes the User Pool in Cognito
- API Gateway verifies identity automatically from AWS Cognito
- No custom implementation required
- Cognito only helps with authentication, not authorization
Summary
| IAM | Custom Authorizer | Cognito User Pool |
|---|---|---|
| Great for users/roles already within your AWS account | Great for 3rd party tokens | You can manage your user pool (backed by FB, Google) |
| Handle authentication + authorization | Very flexible in terms of what IAM policy is returned | No need to write any custom codes |
| Leverages Sig v4 | Handle authentication + authorization | Handle authentication |
| Pay per Lambda invocation | MUST implement authorization logic in the backend |
AWS Cognito
Cognito lets you give your users access to AWS resources after they have successfully authenticated with a web-based identity provider like Amazon, Facebook, or Google.
- Sign-up and sign-in to your apps
- Access for guest users
- Acts as an Identity Broker between your application and Web ID providers, so you don’t need to write any additional code
- Synchronizes user data for multiple devices
- Recommended for all mobile applications AWS services
Cognito brokers between the app and Facebook or Google to provide temporary credentials which map to an IAM role allowing access to the required resources. No need for the application to embed or store AWS credentials locally on the device and it gives users a seamless experience across all mobile devices.
Cognito User Pools
User Pools are user directories used to manage sign-up and sign-in functionality for mobile and web applications. Users can sign-in directly to the User Pool, or using Facebook, Amazon, or Google. Cognito acts as an Identity Broker between the identity provider and AWS. A successful authentication generates a JSON Web Token.
- Create a serverless database of the user for your apps
- Simple login, eg: username + password
- Possibility to verify emails/phone numbers or add MFA
- Can enable Federated Identities
- Return JSON Web Tokens (JWT)
- Can be integrated with API Gateway for authentication
Cognito Federated Identity Pools
Identity Pools provides temporary AWS credentials to access AWS services like S3 or DynamoDB.
- Goal:
- Provide direct access to AWS Resources from the Client Side
- How:
- Login to federated identity provider - or remain anonymous
- Get temporary AWS credentials back from the Federated Identity Pool
- These credentials come with a pre-defined IAM policy stating their permissions
- Example:
- provide (temporary) access to write to S3 bucket using Facebook login
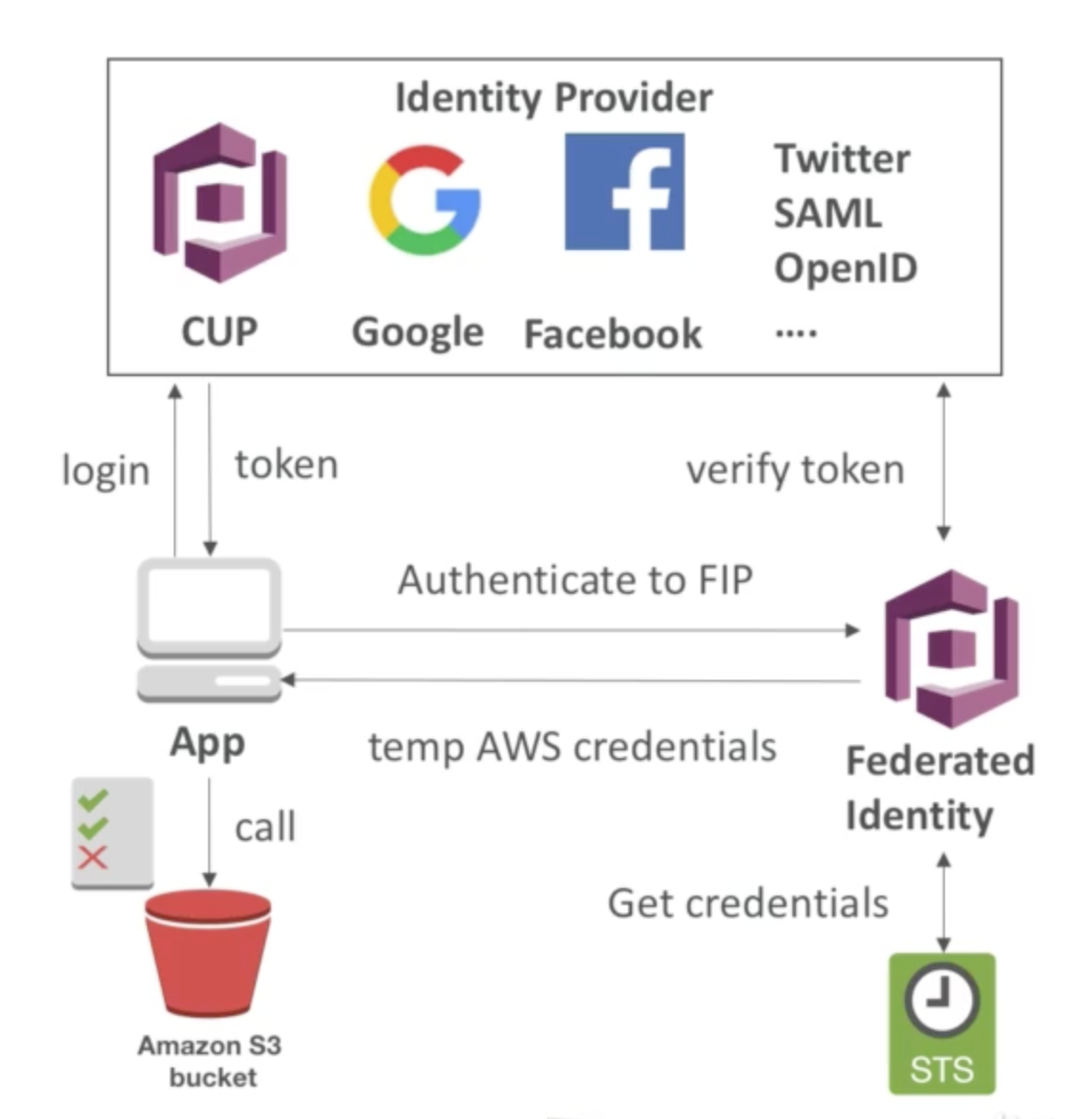
Cognito Sync (Deprecated)
use AWS AppSync instead
Good to know:
- Store preferences, configuration, state of the app
- Cross-device synchronization
- Offline capability
- Requires Federated Identity Pool in Cognito (not User Pool)
- Store data in datasets
Synchronisation
Cognito tracks the association between user identity and the various devices they sign-in from. To provide a seamless user experience for your application, Cognito uses Push Synchronization to push updates and synchronize user data across multiple devices. Cognito uses SNS is to send a notification to all the devices associated with a given user identity whenever data stored in the cloud changes.
AWS SAM - Serverless Application Model
This is a framework for developing and deploying serverless applications
All the configuration is YAML, covers:
- Lambda Functions
- DynamoDB tables
- API Gateway
- Cognito User Pools
Discussion on Serverless Solution Architecture
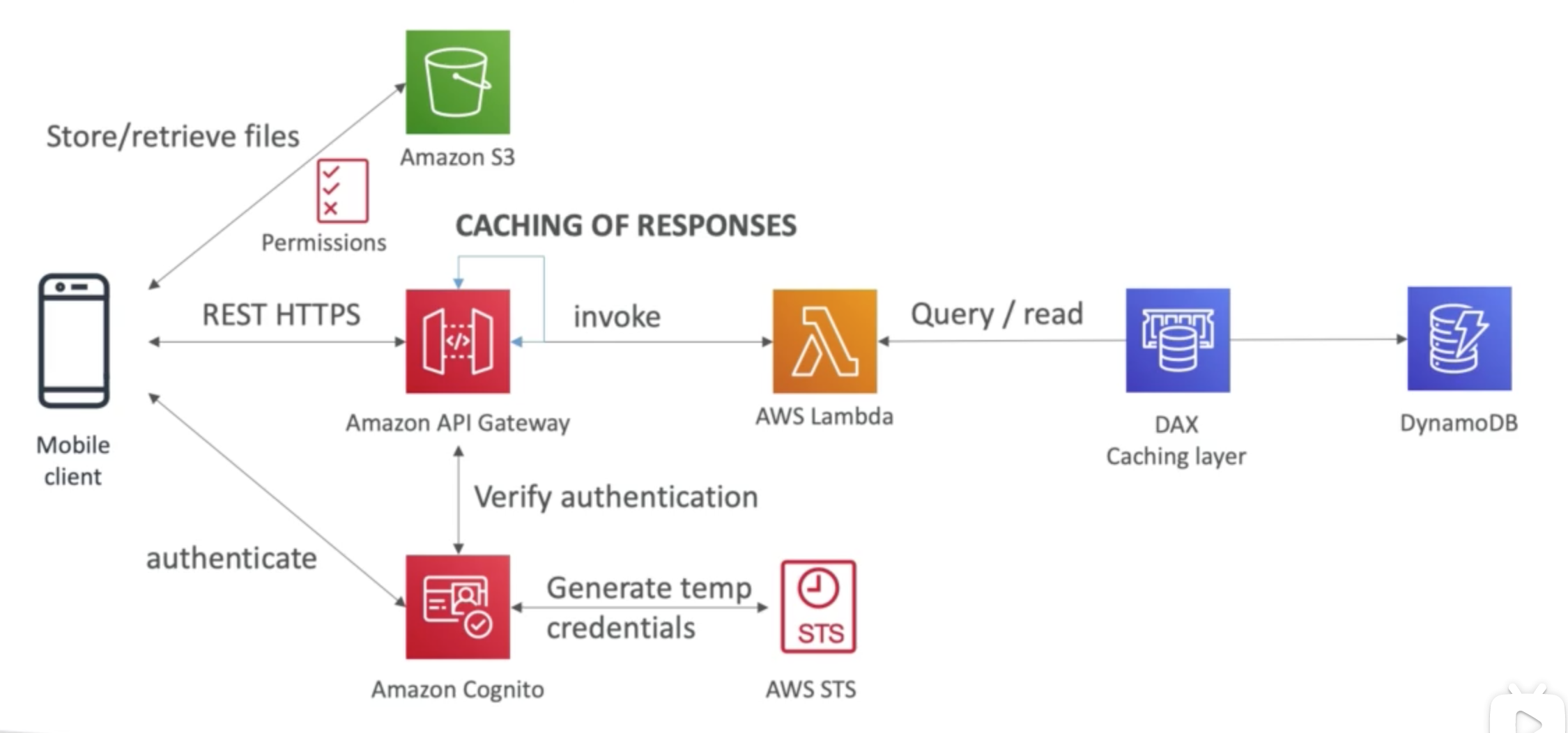
To-do list App
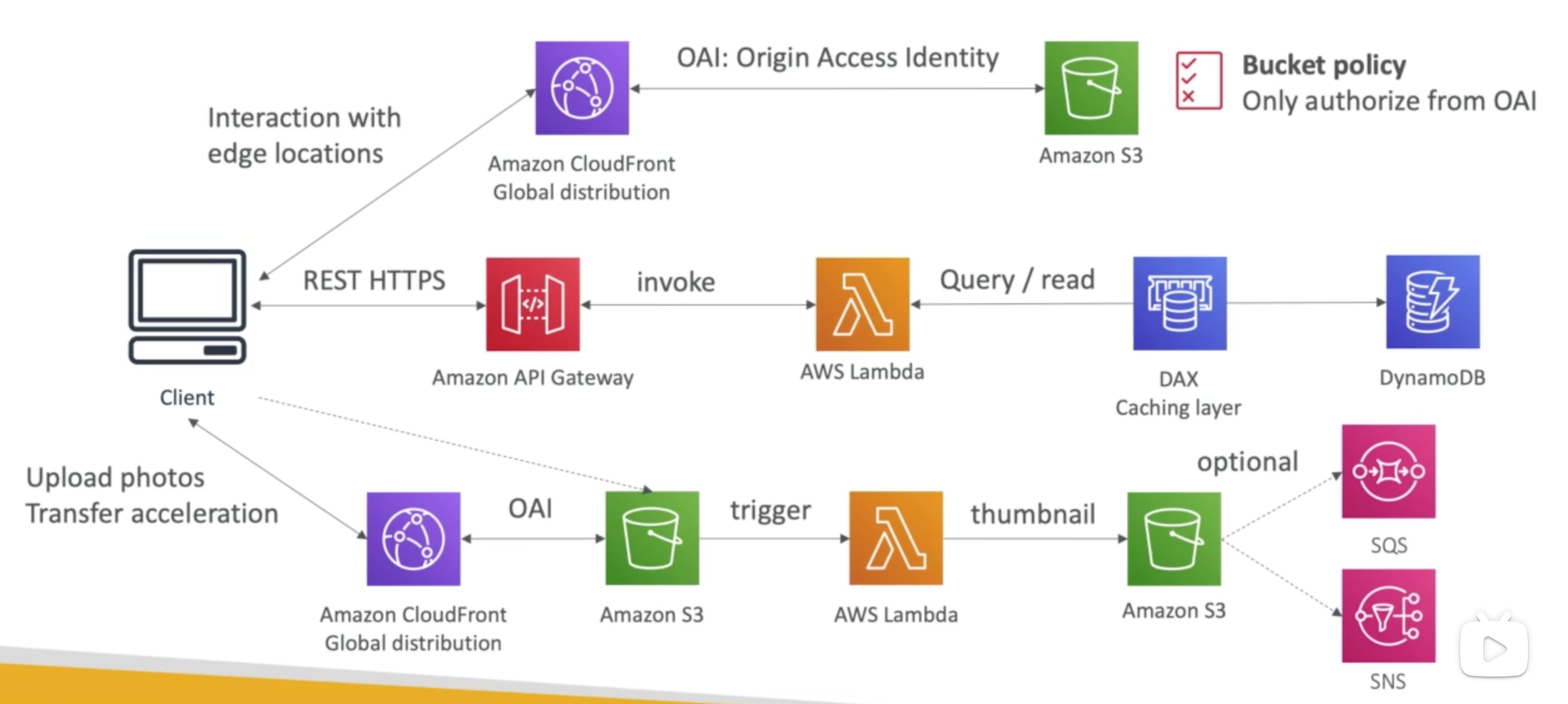
Blog App
Microservices
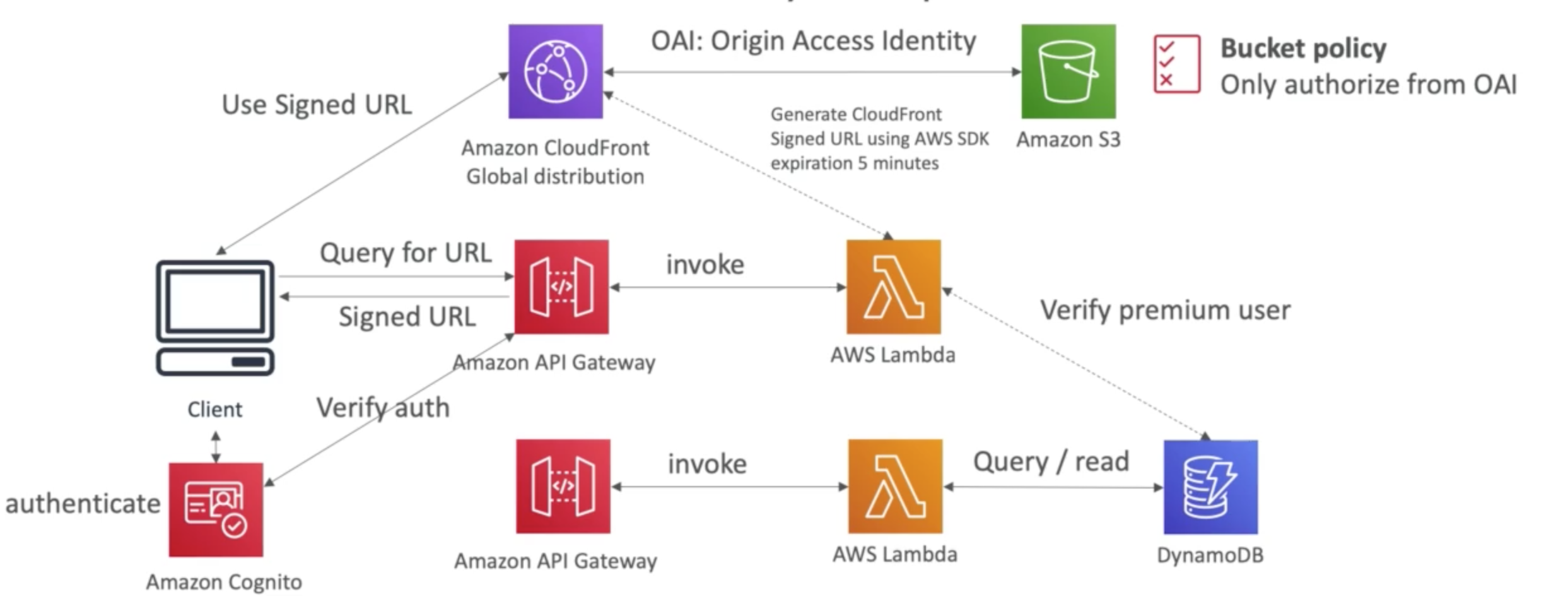
Distribute Paid Content
In short, this can be a great fit for premium user video, here is an example solution we can provide:
- Cognito for authentication
- DynamoDB for storing users that are premium
- 2 serverless applications
- premium user registration
- CloudFront Signed URL generator
- Content is stored in S3 (serverless and scalable)
- Integrated with CloudFront with OAI for security (users cannot bypass)
- CloudFront can only be used with Signed URLs to prevent unauthorized users
- What about S3 Signed URL? They’re not efficient for global access
Software update release
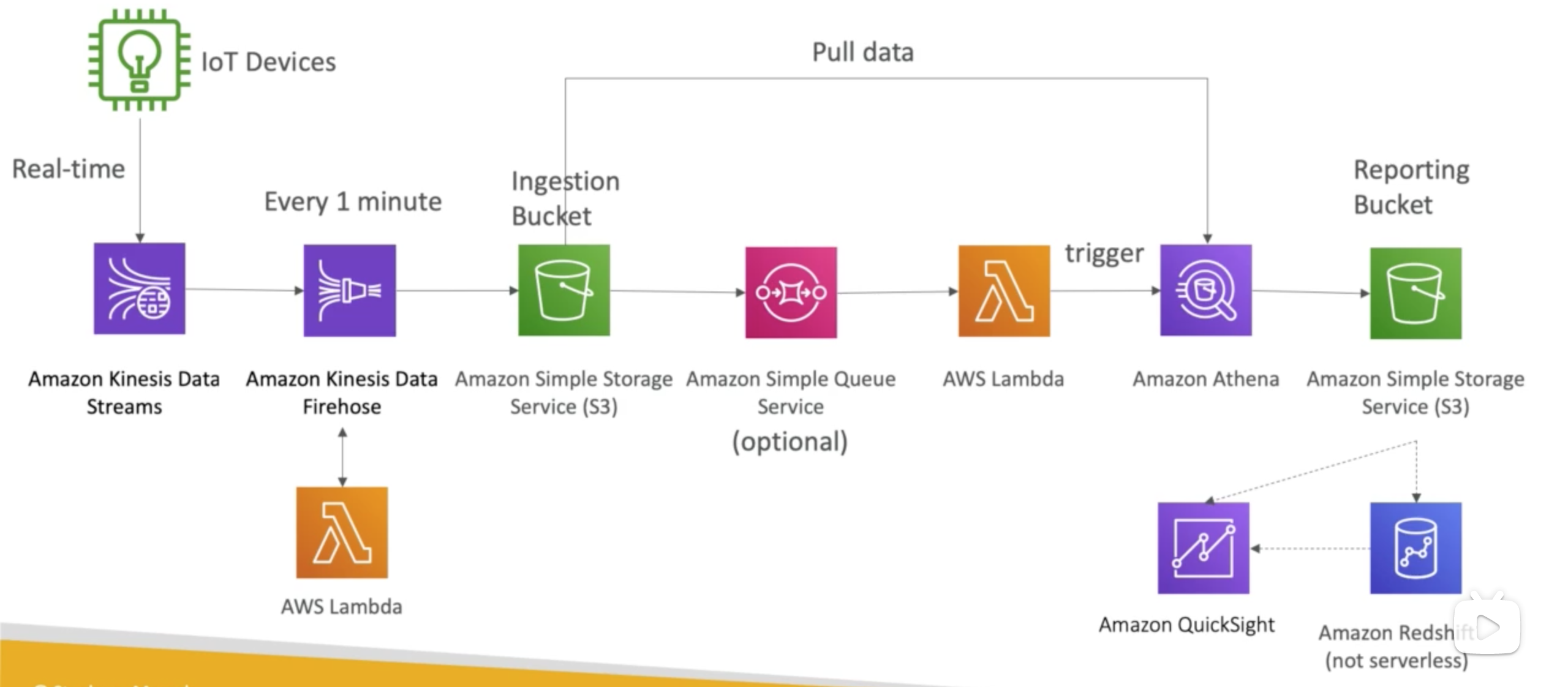
Big Data Pipeline