Spark SQL 简介
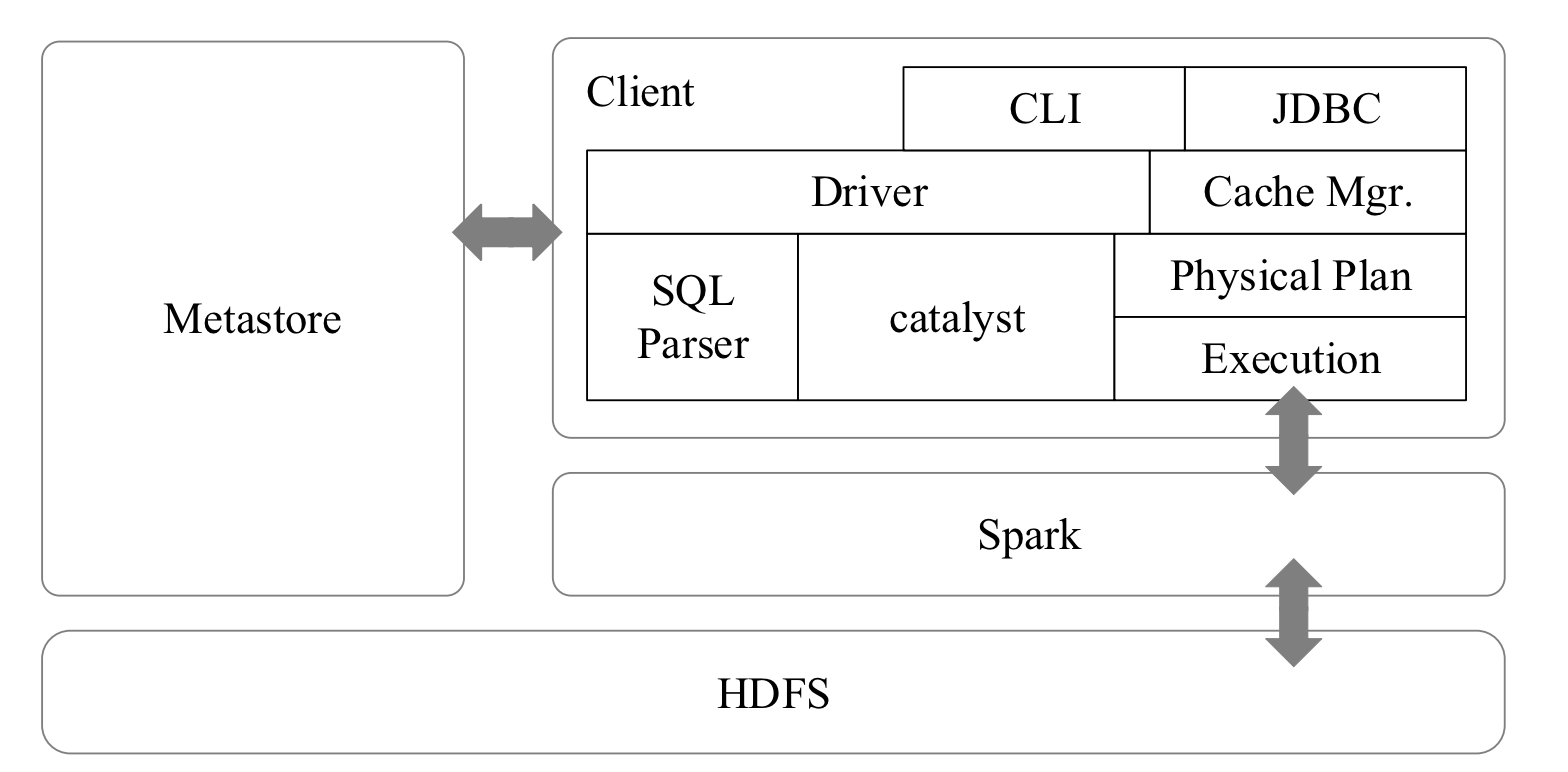
Spark SQL 架构
DataFrame 概述
RDD 和 DataFrame 区别
- RDD 是分布式的 Java 对象的集合, 但是, 对象内部结构对于 RDD 而言却是不可知的
- DataFrame 是一种以 RDD 为基础的分布式数据集, 提供了详细的结构信息
DataFrame 的创建
SparkSession 实现了 SQLContext 及 HiveContext 所有功能
SparkSession支持从不同的数据源加载数据, 并把数据转换成DataFrame, 并且支持把DataFrame转换成SQLContext自身中的表, 然后使用 SQL 语句来操作数据
from pyspark import SparkContext, SparkConf
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder.config(conf=SparkConf()).getOrCreate()
实际上, 在启动进入 pyspark 交互式环境以后, pyspark 就默认提供了一个
SparkContext对象 (名称为sc) 和一个SparkSession对象 (名称为spark)
在创建 DataFrame 时, 可以使用 spark.read() 或 spark.read.format() 操作, 从不同类型的文件中加载数据创建 DataFrame
# 读取文本文件 people.txt 创建 DataFrame
spark.read.text("people.txt")
spark.read.format("text").load("people.txt")
# 读取 people.json 文件创建 DataFrame; 在读取本地文件或 HDFS 文件时, 要注意给出正确的文件路径
spark.read.json("people.json")
spark.read.format("json").load("people.json")
# 读取 people.parquet 文件创建 DataFrame
spark.read.parquet("people.parquet")
spark.read.format("parquet").load("people.parquet")
举个栗子
在 "/usr/local/spark/examples/src/main/resources/" 这个目录下, 这个目录下有两个样例数据people.json和people.txt
>>> df = spark.read.json("file:///usr/local/spark/examples/src/main/resources/people.json")
>>> df.show()
+----+-------+
| age| name|
+----+-------+
|null|Michael|
| 30| Andy|
| 19| Justin|
+----+-------+
DataFrame 的保存
df.write.text("people.txt")
df.write.format("text").save("people.txt")
df.write.json("people.json")
df.write.format("json").save("people.json")
df.write.parquet("people.parquet")
df.write.format("parquet").save("people.parquet")
下面从示例文件 people.json 中创建一个 DataFrame, 名称为 peopleDF, 把 peopleDF 保存到另外一个 JSON 文件中, 然后, 再从 peopleDF 中选取一个列 (即 name 列), 把该列数据保存到一个文本文件中
>>> peopleDF = spark.read.format("json").\
... load("file:///usr/local/spark/examples/src/main/resources/people.json")
>>> peopleDF.select("name", "age").write.format("json").\
... save("file:///usr/local/spark/mycode/sparksql/newpeople.json")
>>> peopleDF.select("name").write.format("text").\
... save("file:///usr/local/spark/mycode/sparksql/newpeople.txt")
会新生成一个名称为 newpeople.json 的目录 (不是文件) 和一个名称为 newpeople.txt 的目录 (不是文件)
DataFrame 的常用操作
>>> df.printSchema()
>>> df.select(df["name"], df["age"] + 1).show()
>>> df.filter(df["age"] > 20).show()
>>> df.groupBy("age").count().show()
>>> df.sort(df["age"].desc(), df["name"].asc()).show()
从 RDD 转换得到 DataFrame
利用反射机制推断 RDD 模式
people.txt
Michael,29
Andy,30
Justin,19
from pyspark.sql import Row
people = spark.sparkContext.\
textFile("file:///usr/local/spark/examples/src/main/resources/people.txt").\
map(lambda line: line.split(",")).\
map(lambda p: Row(name=p[0], age=int(p[1])))
schemaPeople = spark.createDataFrame(people)
# 必须注册为临时表才能供下面的查询使用
schemaPeople.createOrReplaceTempView("people")
# DataFrame 中的每个元素都是一行记录, 包含 name 和 age 两个字段, 分别用 p.name 和 p.age 来获取值
personsDF = spark.sql("select name,age from people where age > 20")
personsRDD = personsDF.rdd.map(lambda p:"Name: "+p.name+ ", "+"Age:"+str(p.age))
personsRDD.foreach(print)
# Output
# Name: Michael, Age: 29
# Name: Andy, Age: 30
使用编程方式定义 RDD 模式
当无法提前获知数据结构时, 就需要采用编程方式定义 RDD 模式. 比如, 现在需要通过编程方式把 people.txt 加载进来生成 DataFrame, 并完成 SQL 查询
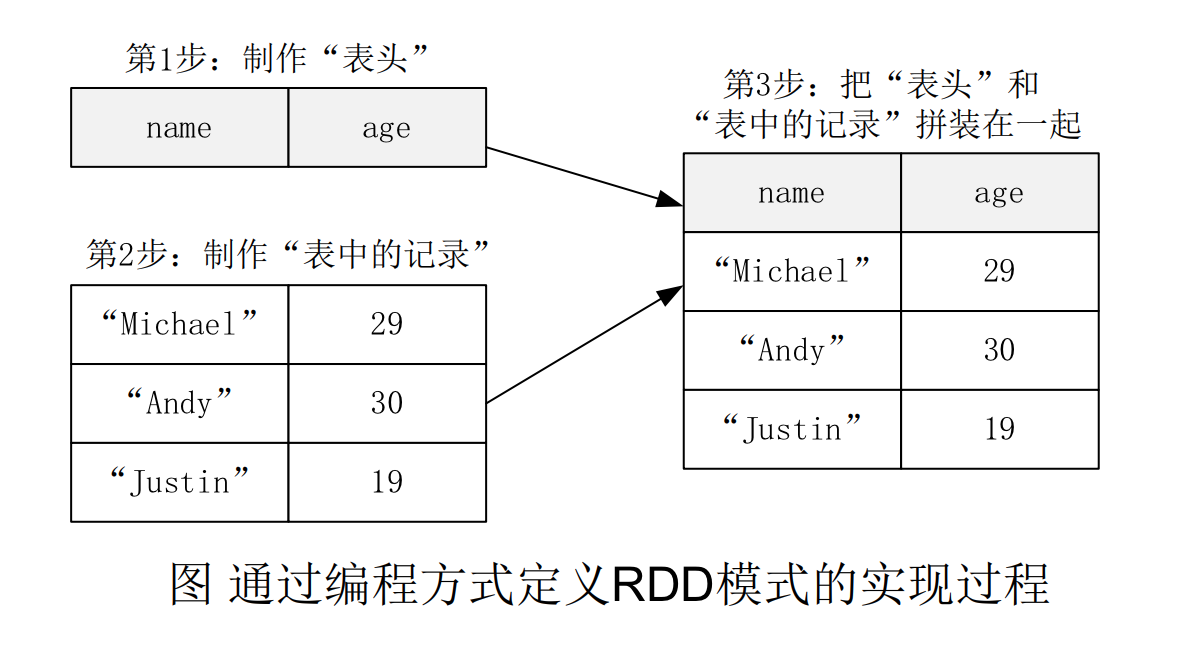
from pyspark.sql.types import *
from pyspark.sql import Row
# 下面生成 "表头"
schemaString = "name age"
fields = [StructField(field_name, StringType(), True) for field_name in schemaString.split(" ")]
schema = StructType(fields)
# 下面生成 "表中的记录"
lines = spark.sparkContext.\
textFile("file:///usr/local/spark/examples/src/main/resources/people.txt")
parts = lines.map(lambda x: x.split(","))
people = parts.map(lambda p: Row(p[0], p[1].strip()))
# 下面把 "表头" 和 "表中的记录" 拼装在一起
schemaPeople = spark.createDataFrame(people, schema)
# 注册一个临时表供下面查询使用
schemaPeople.createOrReplaceTempView("people")
results = spark.sql("SELECT name, age FROM people")
results.show()
# Output
# +-------+---+
# | name|age|
# +-------+---+
# |Michael| 29|
# | Andy| 30|
# | Justin| 19|
# +-------+---+
使用 Spark SQL 读写数据库
读取 MySQL 数据库中的数据
MySQL 的读取利用了 JDBC Driver
>>> jdbcDF = spark.read \
.format("jdbc") \
.option("driver","com.mysql.jdbc.Driver") \
.option("url", "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spark") \
.option("dbtable", "student") \
.option("user", "root") \
.option("password", "123456") \
.load()
>>> jdbcDF.show()
+---+--------+------+---+
| id| name|gender|age|
+---+--------+------+---+
| 1| Xueqian| F| 23|
| 2|Weiliang| M| 24|
+---+--------+------+---+
向 MySQL 数据库写入数据
往 spark.student 表中插入两条记录
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pyspark.sql import Row
from pyspark.sql.types import *
from pyspark import SparkContext,SparkConf
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder.config(conf = SparkConf()).getOrCreate()
# 下面设置模式信息
schema = StructType([StructField("id", IntegerType(), True), \
StructField("name", StringType(), True), \
StructField("gender", StringType(), True), \
StructField("age", IntegerType(), True)])
# 下面设置两条数据, 表示两个学生的信息
studentRDD = spark \
.sparkContext \
.parallelize(["3 Rongcheng M 26","4 Guanhua M 27"]) \
.map(lambda x:x.split(" "))
# 下面创建 Row 对象, 每个 Row 对象都是 rowRDD 中的一行
rowRDD = studentRDD.map(lambda p:Row(int(p[0].strip()), p[1].strip(), p[2].strip(), int(p[3].strip())))
# 建立起 Row 对象和模式之间的对应关系, 也就是把数据和模式对应起来
studentDF = spark.createDataFrame(rowRDD, schema)
# 写入数据库
prop = {}
prop['user'] = 'root'
prop['password'] = '123456'
prop['driver'] = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
studentDF.write.jdbc("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spark",'student','append',prop)